| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Category of Drug | Halothane is a drug for Anaesthesia |
| Mechanism of Action 1 | Halothane causes actions on multiple ion channels, which ultimately depresses nerve conduction, breathing, cardiac contractility. |
| Chemical structure 2 | 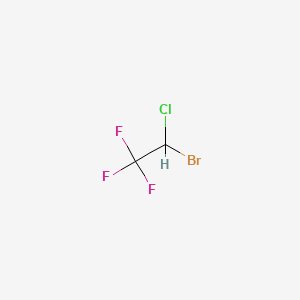 |
| IUPAC Name | 2-bromo-2-chloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane |
| Molecular details | 1. Molecular Formula:- BrClHC2F3 or C2HBrClF3 2. Molecular Weight: 197.38 g/mol |
| Pharmacokinetic properties 1 | 1. Absorption-Not Available 2. The volume of distribution-Not Available 3. Protein binding-Not Available 4. Metabolism- Halothane is metabolized in the liver, primarily by CYP2E1 |
| Indications | Halothane is used for 1. Induction and maintenance of anaesthesia |
| Well Known Pharmaceutical Brands | Hypnothane- Neon |
| Available dosage forms | Volatile Liquid |
| Dose | Introductory dose: 0.5 to 3%. Maintenance dose: 0.5 to 1.5%. |
| Contraindications | 1. History of unexplained jaundice or pyrexia following previous exposure to halothane 2. Family history of malignant hyperthermia 3. Raised cerebrospinal fluid pressure 4. Porphyria 5. Not recommended for obstetrical anaesthesia 6. Interactions |
| Precautions | 1. Anaesthetic history should be carefully taken to determine previous exposure and previous reacons to halothane 2. Avoid for dental procedures in patients under 18 years unless treated in hospital 3. Lactation 4. Renal failure 5. Hyperkalaemia |
| Adverse Effects | 1. Arrhythmias 2. Bradycardia 3. Respiratory depression 4. Hepatic damage 5. Malignant hyperthermia 6. Cyanosis 7. Post-operative nausea and voming |
| Pregnancy Category | C |