| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Category of Drug | Midazolam is a drug for Anaesthesia |
| Mechanism of Action 1 | Midazolam increases the activity of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), in the central nervous system. |
| Indications 2 | Midazolam is used for 1. Intravenous sedative administered before or during minor surgical procedures 2. Sedative administered by intravenous route in intensive care induction of anesthesia |
| Structure 3 | 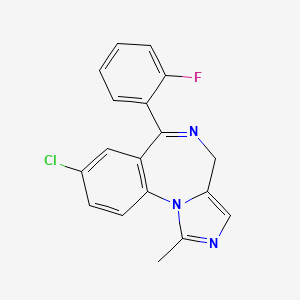 |
| Molecular details | 1. Molecular Formula: C18H13ClFN3 2. Molecular Weight: 325.8 g/mol |
| IUPAC Name | 8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-imidazo[1,5-a][1,4]benzodiazepine |
| Well Known Pharmaceutical Brands | 1. MEZOLAM- NEON LABS 2. MIDACIP- CIPLA |
| Available dosage forms | INJECTION |
| Dose 4 | Slow IV injection in adults- 2 mg/min; 5 to 10 min before procedure; initially 2 to 2.5 mg. Max. 7.5 mg) |
| Pharmacokinetic properties | 1. Absorption: Rapidly absorbed after oral administration. 2. Volume of distribution: Female gender, old age, and obesity may increase the volume of distribution. 3. Protein binding: 97% bound to plasma protein. 4. Metabolism: Midazolam is primarily metabolized in the liver and gut by CYP3A4 5. Half-life = 1.8 to 6.4 hours |
| Contraindications | 1. Acute narrow-angle glaucoma 2. Comatose patients 3. Shock 4. Acute alcohol intoxication 5. For intrathecal and epidural use 6. Acute pulmonary insufficiency 7. Myasthenia gravis |
| Precautions | 1. Chronic renal failure 2. Cardiac disease 3. Open-angle glaucoma 4. Respiratory disorders 5. Neonates 6. Prolonged use and abrupt withdrawal should be avoided 7. Hepatic impairment 8. Pregnancy |
| Adverse Effects | 1. Hypersensitivity 2. Cardiac arrest 3. Laryngospasm 4. Apnoea 5. Headache 6. Hiccups 7. Nausea 8. vomiting 9. Cough 10. Kernicterus 11. Nystagmus |
| Pregnancy Category | D |