Microencapsulation means applying relatively thin coatings to small particles of solids or droplets of liquids or dispersions. It involves the coating of particles ranging from several tenths of a micron to 5000 microns in size. This technique is an effective means of converting liquids to solids by altering their colloidal and surface properties. It also protects the drug core from the environment and controls the coated material’s release characteristics.
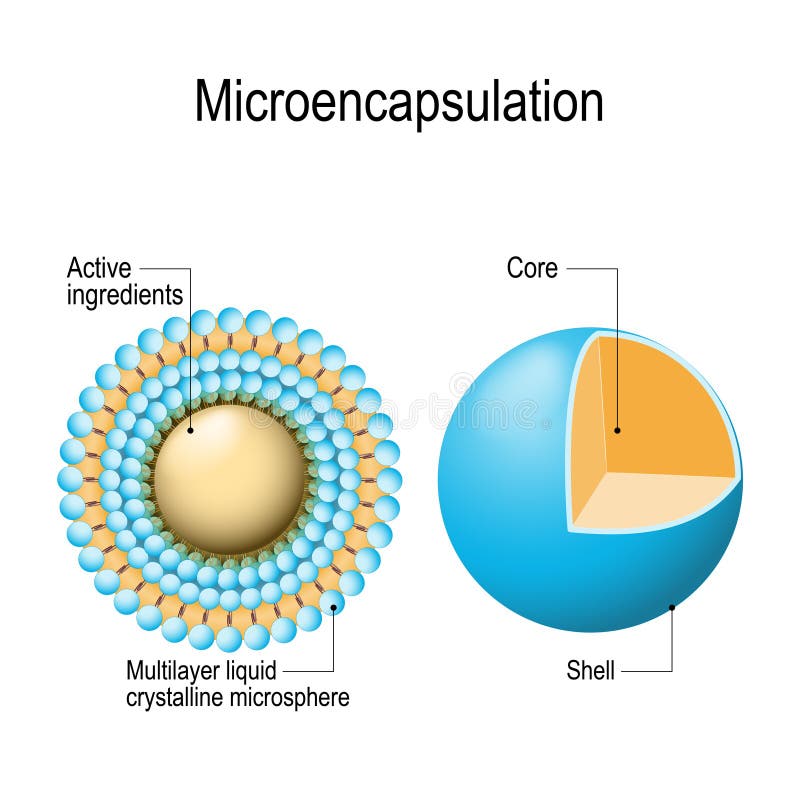
In the context of microencapsulation, two important terminologies are inherent. One being “core material” and the other being “coating material.” These are defined as follows :

- The core material is the specific material to be coated and can be liquid or solid. It can also be a mixture of active constituents, stabilizers, diluents, excipients, and release rate retardants or accelerants. E.g., Acetaminophen, Vitamin A palmitate.
- Coating material – These agents are capable of forming a film that is cohesive, chemically compatible, and non – reactive with the core material. They can be water-soluble resins, water-insoluble resins, waxes, lipids, or enteric resins. E.g., Gelatin, Cellulose acetate phthalate, etc.
Advantages of Microencapsulating Drugs
- It Masks the taste of bitter drugs to make them more palatable and improving patient compliance. Eudragit E100 is the most commonly used coating material for this purpose. The microencapsulated drugs do not interact with the taste receptors as it insoluble in the mouth. E.g., Ofloxacin.
- Conversion of a liquid dosage form to pseudo solid or free-flowing powder. E.g., Eprazinone

- To provide environmental protection of the core material from moisture, light, and oxygen. E.g., Nifedipine
- To prevent the physical and chemical incompatibilities between drugs and to avoid volatilization of medicines like aspirin at room temperature.
- To formulate sustained or prolonged release dosage forms that continuously release the drugs at a constant rate for a set period.
- It enhances the solubility of poorly soluble drugs and the safe handling of toxic medications.
- For the targeted release of the encapsulated material at the desired site.
- To alter the physical and surface properties of certain drugs. E.g., Reducing the hygroscopicity of sodium chloride.
Disadvantages of Microencapsulation :
- The cost of the materials used and the formulation process might be higher than standard formulations.
- Reproducibility is less.
- The effect of the polymer matrix, polymer additives, and their degradation products on the environment in response to heat, hydrolysis, or biological agents vary significantly.
- The core particle’s stability is affected by the change in the process conditions like change in temperature, pH, solvent addition, or evaporation of the solvent.
Read more:
- Multiparticulate drug delivery systems consist of three common constituents: microparticles, microcapsules, and microspheres. These microcarriers do not traverse through the interstitium and therefore produce local action. Read Constituents of multiparticulate drug delivery system
- The method of microencapsulation depends on the core material, the application of the microcapsule, size of particles needed, release characteristics of the microcapsule, and the cost of production. Read Methods of Microencapsulation and Process
- Microencapsulation is widely used to manufacture prolonged-release dosage forms, pulsatile release dosage forms, and targeted drug delivery systems. Apart from this, it has some other standard Applications of microencapsulation. Read Applications of microencapsulation and challenges
- Article review


Pingback: Constituents of multiparticulate drug delivery system > PharmaCampus
Pingback: Applications of microencapsulation and challenges > PharmaCampus
Pingback: Methods of Microencapsulation and Process > PharmaCampus
Pingback: Is Big Data Analytics revamping the Pharmaceutical Industry? > PharmaCampus