Multiparticulate drug delivery systems consist of three common constituents: microparticles, microcapsules, and microspheres. These microcarriers do not traverse through the interstitium and therefore produce local action.
Multiparticulate Drug Delivery Systems: Major constituents
- Microparticles – These particles range from 1 to 1000 microns in size and are generally of spheroid shape. They have a well-known matrix or reservoir structure and include microspheres and microcapsules.
- Microcapsules – These are heterogeneous particles in which a membrane shell surrounds the core to form a reservoir. The core may be either solid, liquid, or even hollow space, while the shell is a continuous porous or non – porous layer.
- Microspheres – These microparticles are composed of a solid polymer matrix in which the drug substance is homogenously dissolved or dispersed. The release characteristics of microspheres differ significantly from that of microcapsules.
Read more:
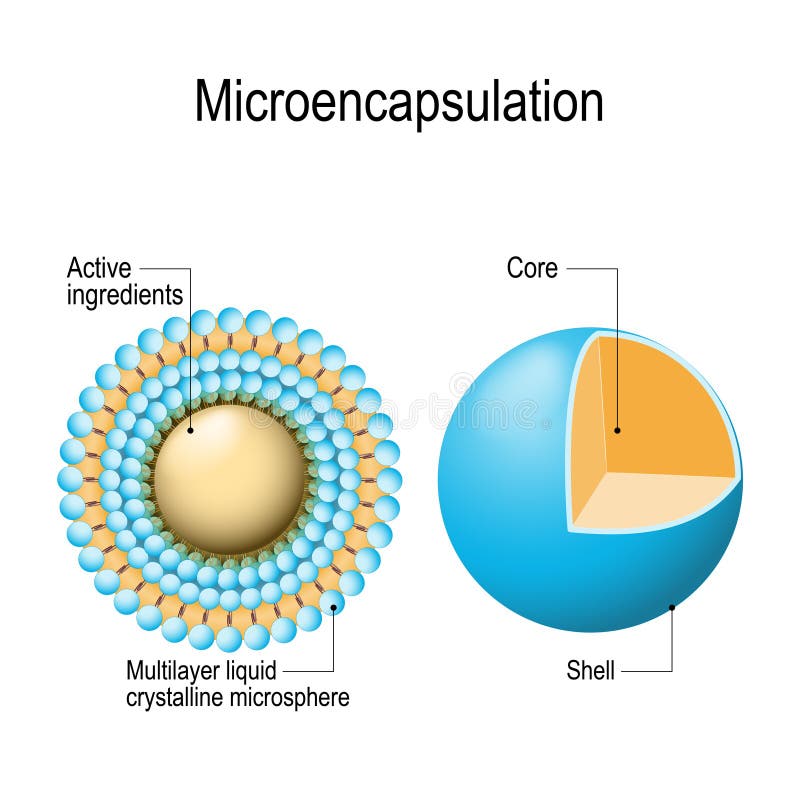
Microencapsulation Process: Brief overview
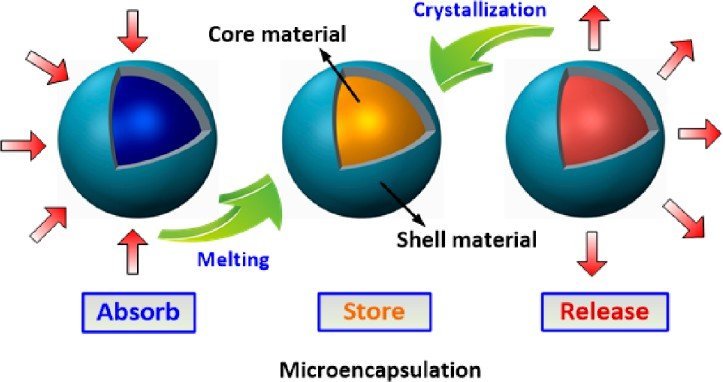
Microencapsulation means applying relatively thin coatings to small particles of solids or droplets of liquids or dispersions. It involves the coating of particles ranging from several tenths of a micron to 5000 microns in size. This technique is an effective means of converting liquids to solids by altering their colloidal and surface properties. It also protects the drug core from the environment and controls the coated material’s release characteristics.
In the context of microencapsulation, two important terminologies are inherent. One being “core material” and the other being “coating material.” Read Microencapsulation: Advantages and disadvantages
- The method of microencapsulation depends on the core material, the application of the microcapsule, size of particles needed, release characteristics of the microcapsule, and the cost of production. Read Methods of Microencapsulation and Process
- Microencapsulation is widely used to manufacture prolonged-release dosage forms, pulsatile release dosage forms, and targeted drug delivery systems. Apart from this, it has some other standard Applications of microencapsulation. Read Applications of microencapsulation and challenges
- Article review

Pingback: Microencapsulation: Advantages and disadvantages > PharmaCampus
Pingback: Applications of microencapsulation and challenges > PharmaCampus
Pingback: Methods of Microencapsulation and Process > PharmaCampus