In the pharmaceutical industry, polymers are extensively used to produce various dosage forms. These include both conventional dosage forms and novel drug delivery systems. In this article, we will discuss the application of polymers in the formulation of controlled release drug delivery systems.
Polymers Applications in Pharma
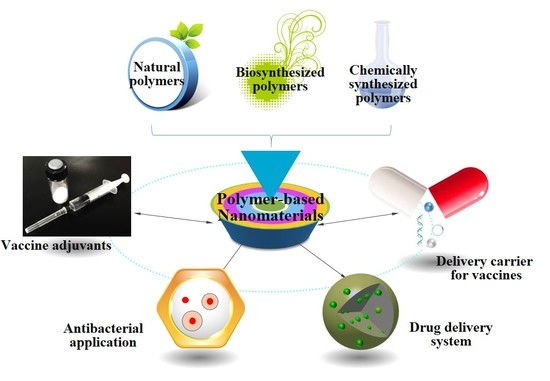
The different types of controlled drug delivery systems and the pharmaceutical polymers used in their formulation are as follows:
- Reservoir system
- Ocusert system
- Matrix System
- Biodegradable System
- Osmotically controlled drug release
- Temperature responsive drug delivery
- pH-responsive drug delivery
Reservoir systems
- Reservoir systems – In these systems, the drug core is surrounded by a polymer film made of silicone, ethylcellulose, or polyethylene vinyl acetate. The drug’s release rate is controlled by the characteristics of the polymer, the thickness of the coating, and the physicochemical properties of the drug. The drug release involves the partitioning of the drug into the polymeric coat, followed by its diffusion into the polymer’s outer coat and finally into the surrounding biological environment.
Ocusert system
- Ocusert system – These are used to deliver drugs to the eye and consist of polymeric systems that ensure better ocular bioavailability and retention of drugs. Polymers with good mucoadhesive properties like Carbopol 934 P (cross–linked polyacrylic acids )are often incorporated as adjuvants in these systems as they prolong the drug’s residence time in the eye and thereby increase the contact time of the drug with the absorbing mucosa. This, in turn, enhances drug absorption and therapeutic effect. These systems are more effective than the conventional dosage, such as eye drops rapidly cleared from the eyes due to blinking or tears.
Matrix systems
- Matrix systems – Hydrophilic and hydrophobic polymers are used in this system, to prolong and control the drug release, which is dissolved or dispersed in it. Hydrophilic polymers are widely used compared to hydrophobic ones as they have high gelling capacities and provide the desired release characteristics to the drug. Matrix tablets with water-insoluble polymers are stable in the alimentary tract and allow the drug’s gradual release. This release occurs due to the gradual decomposition of the drug from the poor soluble, therapeutic agent – polymer complex: Eg. Methylcellulose, Alginates, Chitosan, and Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose.
Biodegradable system
- Biodegradable system – These polymers undergo controlled degradation in the biological environment following implantation. This occurs by either hydrolysis of the main polymer chain or the crosslinks that convert the previously insoluble polymer to a soluble to facilitate elimination. The advantages of biodegradable polymers are that their degradability reduces the need for subsequent surgical removal of the implant, which saves both time and money to the patient. Examples of polymers used in this system include polylactic acid ( PLA ), polyglycolic acid ( PGA ), and their copolymers like PGLA.
Osmotically controlled drug delivery systems
- Osmotically controlled drug delivery systems – Oral osmotically controlled release delivery systems use osmotic pressure for controlled delivery of the active agents. Drug release from these systems is independent of pH and other physiological parameters to a large extent but can be modulated by changing the properties of the drug and system. Swellable polymers like polyethylene oxide and vinyl acetate copolymer are often incorporated into the system as these swell when exposed to water and produce the pressure needed for the drug’s constant release via the orifice in the system.
Temperature responsive drug delivery
- Temperature responsive drug delivery – These controlled drug release systems contain drugs released in response to the temperature. A particular class of polymers called thermoresponsive polymeric systems is used to facilitate this. Copolymers of N – substituted acrylic and methacrylate amides like poly isopropyl acrylamide are often used in these systems. These polymers exhibit temperature-dependent and reversible sol–gel transitions near body temperature. This, in turn, controls the release rate and maintains the incorporated drug’s physicochemical stability and biological activity.
pH-responsive drug delivery
- pH-responsive drug delivery – Within the gastrointestinal tract, the pH values differ significantly, starting from about one in the stomach to neutrality within the intestine. pH-responsive polymers are conjugated with the drugs that target these regions to ensure the delivery of drugs in a controlled manner at a specific time and site. Enteric polymers like cellulose acetate phthalate and cellulose acetate butyrate are used for coating tablets that target the alimentary canal. These polymers are insoluble in low pH environments but soluble in the less acidic gastrointestinal tract regions. Following the dissolution of the enteric coating, the tablet and the drug dissolves to facilitate drug absorption.
Tabular presentation
| Polymers Applications in Pharma | Description |
|---|---|
| Reservoir systems | The drug’s release rate is controlled by the characteristics of the polymer, the thickness of the coating, and the physicochemical properties of the drug. |
| Ocusert system | Polymers with good mucoadhesive properties like Carbopol 934 P (cross-linked polyacrylic acids )are often incorporated as adjuvants in these systems. |
| Matrix systems | Hydrophilic and hydrophobic polymers are used in this system, to prolong and control the drug release. |
| Biodegradable system | These polymers undergo controlled degradation in the biological environment following implantation. Examples PLA, PGA, PGLA. |
Osmotically controlled drug delivery systems | use osmotic pressure for controlled delivery of the active agents. |
| Temperature responsive drug delivery | the thermoresponsive polymeric system is used to facilitate drug release in response to the temperature. |
| pH-responsive drug delivery | As one of the popular applications, Enteric polymers like cellulose acetate phthalate and cellulose acetate butyrate are used for coating tablets that target the alimentary canal. |

Pingback: Implantable Drug Delivery System > PharmaCampus
Pingback: Implants and Osmotic pumps: Types and Uses > PharmaCampus