Prochlorperazine is an Antiemetic prescribed for nausea and vomiting. Antiemetics treat motion sickness, chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, and the side effects of general anesthetics and opioid analgesics.
Few medicines act on the chemoreceptor trigger zone-CTZ (in the brain) by preventing the stimulation. The chemoreceptor trigger zone is a vomiting center. Some medications act as prokinetic agents by speeding up the rate at which the stomach empties.
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Category of Drug | Prochlorperazine is antiemetics drug |
| Mechanism of Action | Prochlorperazine mainly blocks D2 dopamine receptors in the brain. |
| Structure 1 | 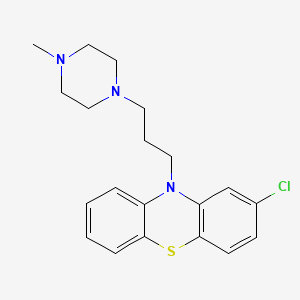 |
| Molecular weight 1 | Molecular formula- C20H24ClN3S molecular weight- 373.9 g/mol |
| IUPAC Name 1 | 2-chloro-10-[3-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl]phenothiazine |
| Indications | Prochlorperazine is used for 1. Nausea and vomiting |
| Pharmacokinetic properties | 1. The onset of action- 30 to 40 minutes. 2. The duration of action-3 to 4 hours 3. protein binding- not known 4. Metabolism- undergoes hepatic metabolism involving oxidation. The oxidation reaction is mediated by CYP2D6 5. mainly excreted via the feces and bile 6. half-life- 8 hours |
| Well Known Pharmaceutical Brands | Stemetil- Abbott Emidoxyn- Shreya Emikind- Mankind |
| Available dosage forms | 1. TABLETS 2. INJECTION  |
| Dose | Adult- Nausea, vomiting acute attack: initially 20 mg then 20 mg every 2 h. Prevention; 5 to 10 mg 2 to 3 times daily. |
| Contraindications | 1. Comatose states 2. CNS depression and pheochromocytoma 3. Most antipsychotics are best avoided during pregnancy 4. Hypersensitivity 5. Prolactin dependant tumours |
| Precautions | 1. Patients with hepatic impairment 2. Renal impairment 3. Cardiovascular disease 4. Parkinson’s disease 5. Epilepsy 6. Depression 7. Myasthenia gravis 8. Prostatic hypertrophy 9. Susceptibility to angle-closure glaucoma |
| Adverse Effects | 1. Less sedating 2. Extrapyramidal symptoms 3. Particularly dystonias 4. Respiratory depression may occur in susceptible patients 5. Amenorrhoea 6. Blurred vision 7. Cholestatic jaundice 8. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome 9. Leucopenia 10. Agranulocytosis |
| Pregnancy Category | C |
References
National FOrmulary

Pingback: Gastroenterology: Which are the popular Brands? - PharmaCampus