Phenobarbital, phenytoin, and valproate are widely used to treat Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures. However, each of these drugs is associated with dose-related and idiosyncratic adverse effects, and monitoring of hematological and hepatic function is routinely not advised.
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Category of Drug | Phenytoin is a Anticonvulsants/Antiepileptics |
| Mechanism of Action | Phenytoin promotes or decreases Na+ influx from membranes in motor cortex neurons; stabilizes neuronal membrane. |
| Chemical Structure | 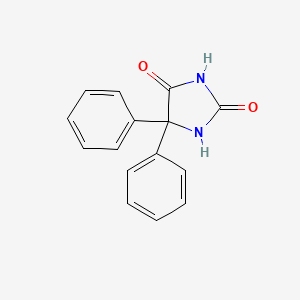 |
| Molecular details | Molecular Formula- C15H12N2O2 Molecular Weight- 252.27 g/mol |
| IUPAC Name | 5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione |
| Indications | Phenytoin is used for 1. Generalized tonic-clonic seizures 2. Partial seizures 3. Status epilepticus. |
| Well Known Pharmaceutical Brands | EPTOIN-ABBOTT EPSOLIN- ZYDUS CADILA DILANTIN- PFIZER |
| Available dosage forms | 1. TABLETS 2. CAPSULES 3. INJECTIONS 4. SUSPENSION TABLETS 2, 5 and 10 mg; CAPSULE 10 mg; SUSPENSION 2 mg/ml; INJECTION 2 ml; ampoule (5 mg/ml). |
| Dose | Adults- 18 mg/kg (do not exceed 50 mg/min as a loading dose); maintenance dose -100 mg 6 to 8 hours. |
| Storage conditions | Store protected from moisture at a temperature not exceeding 30⁰C |
| Pharmacokinetic properties | 1. Phenytoin is completely absorbed. 2. Peak plasma concentration- 1.5-3 hours. 3. Vd-0.75 L/kg. 4. Protein binding- 90% 5. Phenytoin is extensively metabolized. 6. The majority is excreted as inactive metabolites 7. Half-life- 7 to 42 hours. |
| Contraindications | 1. Porphyria 2. Avoid parenteral use in sinus bradycardia 3. Sino-atrial block 4. Second- and 5. Third-degree heart block 6. Stokes-Adams syndrome 7. Pregnancy |
| Precautions | 1. Hepatic impairment 2. lactation 3. Diabetes Mellitus 4. Monitor blood counts 5. Hypotension and heart failure 6. Intravenous administration-resuscitation facilities must be available 7. Injection solution alkaline 8. Interactions |
| Adverse Effects | 1. Gastric intolerance 2. Headache 3. Sleeplessness 4. sedation 5. hallucinations 6. confusion 7. blurred vision 8. ataxia 9. nystagmus 10. diplopia 11. Slurred speech 12. cerebellar-vestibular symptoms, |
| Pregnancy Category | D |
References
- Mechanism of action
- Molecular details
- National Formualry
- Pharmacokinetic properties


Pingback: Alkem Laboratories: Popular Brands, Composition, and Pack Details > PharmaCampus