| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Category of Drug | Metoprolol is selective beta-1 blocker-Antianginal Drugs. Read More: Which are the popular Medicines prescribed for Heart Disorders? |
| Structure 2 | 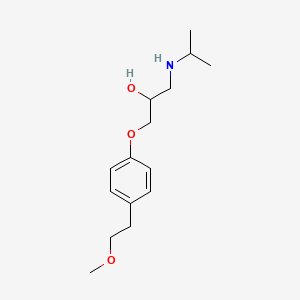 |
| IUPAC Name 2 | 1-[4-(2-methoxyethyl)phenoxy]-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propan-2-ol |
| Molecular details 2 | Molecular formula- C15H25NO3 Molecular weight- 267.36 g/mol |
| Mechanism of Action | It is a selective beta-1 blocker 1 that specifically inhibits the beta receptors present in the cardiac cells. This causes negative chronotropic and ionotropic effects that in turn reduces cardiac output and heart rate. It also reduces cardiac excitability and myocardial oxygen demand. |
| Pharmacokinetics properties 3 | 1. volume of distribution -4.2 L/kg. 2. Protein binding- 11% of the 3. first-pass hepatic metabolism- 50%. 4. The metabolism is mainly driven by the activity of CYP2D6. 5. represented by reactions of hydroxylation and O-demethylation. 6. Route of elimination- mainly excreted via the kidneys. 7. half-life of about 3-7 hours 8. LD50 in the range of 3090 to 4670 mg/kg. |
| Indications | Metoprolol 1 is used for 1. Supraventricular arrhythmia 2. Angina pectoris 3. Hypertension 4. Myocardial infarction 5. Migraine prophylaxis 6. Hyperthyroidism 7. Heart failure |
| Well Known Pharmaceutical Brands | STARPRESS-XL- LUPIN SELOKEN- ASTRAZENECA REVELOL- IPCA PROLOMET-XL- SUN METOLAR-CIPLA METOCARD-TORRENT MET XL- AJANTA EMBETA- INTAS BETALOC-ASTRAZENECA |
| Available dosage forms | 1. TABLETS 2. CAPSULES 3. INJECTION |
| Dose | Hypertension: initially 100 mg daily, increase if required to 200 mg in two divided doses (max 400 mg daily). |
| Contraindications | 1. Asthma 2. Uncontrolled heart failure 3. Prinzmetal’s angina 4. Marked bradycardia 5. Hypotension 6. Sick sinus syndrome 7. Second- or third-degree AV block 8. Cardiogenic shock 9. Metabolic acidosis 10. Severe peripheral arterial disease 11. Pheochromocytoma |
| Precautions | 1. Avoid abrupt withdrawal especially in ischaemic heart disease 2. First-degree AV block 3. Portal hypertension 4. Diabetes 5. History of obstructive airways disease 6. Myasthenia gravis 7. Symptoms of hypoglycaemia and thyrotoxicosis may be masked 8. History of hypersensitivity-may increase sensitivity to allergens and result in more serious hypersensitivity response 9. Also may reduce response to adrenaline |
| Adverse Effects | 1. Gastrointestinal disturbances 2. Bradycardia 3. Heart failure 4. Hypotension 5. Conduction disorders 6. Peripheral vasoconstriction 7. Bronchospasm 8. Dyspnoea 9. Headache 10. Fatigue 11. Sleep disturbances 12. Sexual dysfunction 13. Purpura 14. Thrombocytopenia 15. Visual disturbances 16. Exacerbation of psoriasis |
| Pregnancy Category | C |





Pingback: Which are the popular Medicines prescribed for Heart Disorders? - PharmaCampus