| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Category of Drug | Atenolol is Antianginal Drugs Read more: Which are the popular Medicines prescribed for Heart Disorders? |
| Structure | 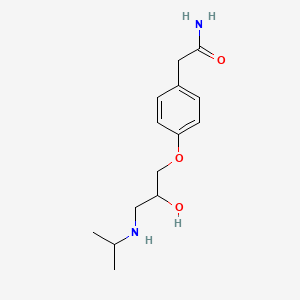 |
| Chemical Formula | C14H22N2O3 |
| IUPAC Name | 2-[4-[2-hydroxy-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propoxy]phenyl]acetamide |
| Molecular details | Molar mass: 266.336 g/mol Boiling point: 508 °C |
| Mechanism of Action | It is a beta-blocker and antagonizes the sympathetic innervation. This, in turn, increases the release of norepinephrine from the peripheral nervous system and prevents the increase in the heart rate, electrical conductivity, and contractility in the heart. |
| Indications | Atenolol is used for 1. Angina and myocardial infarction 2. Arrhythmias 3. Hypertension 4. Migraine prophylaxis |
| Well Known Pharmaceutical Brands | ATEN- ZYDUS CADILA TENOLOL- IPCA LABS BETACARD-TORRENT |
| Available dosage forms | 1. TABLETS 2. CAPSULES  |
| Dose | 25-50 mg/day PO initially; may be increased to 100 mg/day PO |
| Contraindications | 1. Asthma or history of obstructive airways disease 2. Uncontrolled heart failure 3. Prinzmetal angina 4. Marked bradycardia 5. Hypotension 6. Sick sinus syndrome 7. Second-and third-degree atrioventricular block 8. Cardiogenic shock 9. Metabolic acidosis 10. Severe peripheral arterial disease 11. Pheochromocytoma |
| Precautions | 1. Severe hepatic or renal impairment 2. May precipitate or worsen heart failure 3. Acute myocardial infarction 4. Pregnancy 5. Thyrotoxicosis 6. Pheochromocytoma 7. Lactation 8. First-degree atrioventricular block |
| Adverse Effects | 1. Gastrointestinal disturbances 2. Fatigue 3. Cold hands and feet 4. Exacerbation of intermittent claudication and Raynaud phenomenon 5. Bronchospasm 6. Bradycardia 7. Heart failure 8. Conduction disorders 9. Hypotension |
| Pregnancy Category | D |
References:


Pingback: Which are the popular Medicines prescribed for Heart Disorders? - PharmaCampus