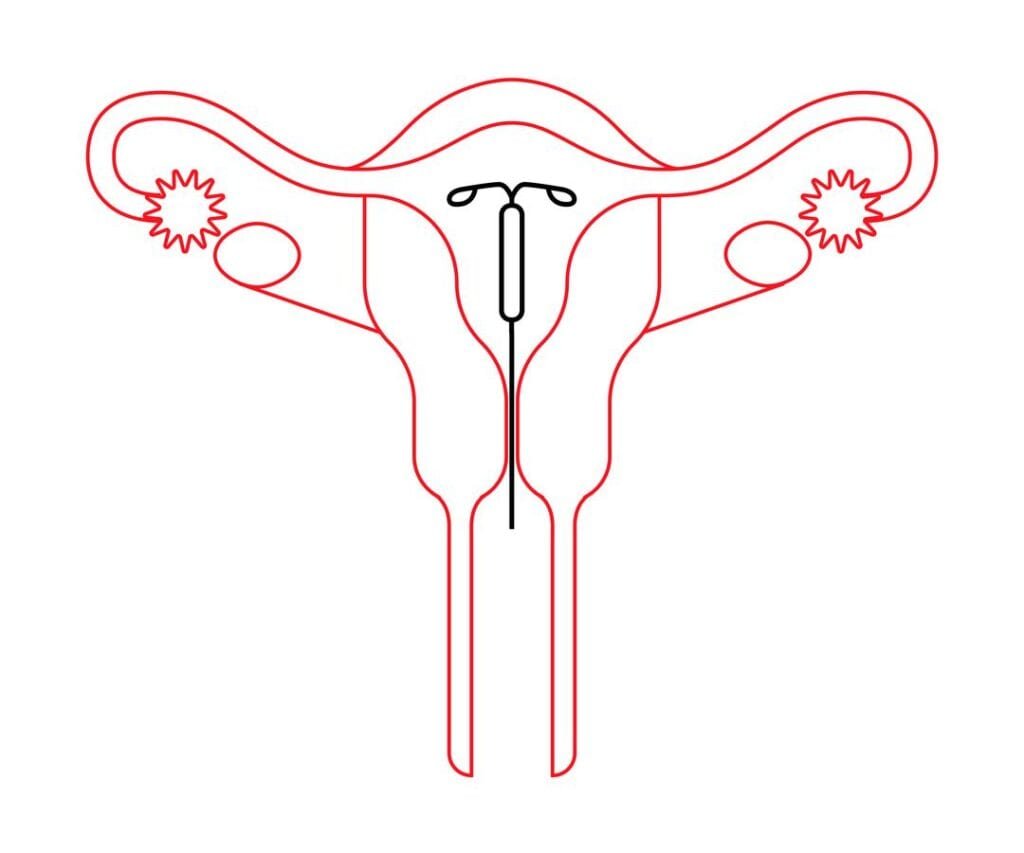
A wide variety of ever-increasing IUD drug delivery systems with different formulations and properties are available in the market. We can find the in vitro tests in different pharmacopeias and monographs. There are methods to analyze the quality control of the final product. However, predictability cannot be estimated appropriately. The advantages are encouraging comprehensive Applications of IUD. Read more about Introduction to Intrauterine Drug Delivery Systems
As technology progresses, the major lacunae of testing and development will be filled, creating better novel drug delivery systems that are safer and effective while ensuring patient compliance and comfort.
IUD Applications

The vagina is a suitable site for local and systemic drug delivery, as per recent scientific reports. Several novel formulation approaches are under process development for targeted delivery as IUDs, including but not limited to microgels, various nanocarriers, microparticulate systems, liposomes, polymer-coated liposomes, nanospheres, etc.
These developments for novel drug delivery systems have a great potential for development and efficient utilization. However, due to the limitations of predictability, the development process may face hindrances.
The major Applications of IUD are to:
- Prevent conception
- Treat local infections
- Treat systemic diseases
- Hormonal treatments
- Targeted delivery of drugs
Popular medicines with an IUD system
| Drug name | Dosage form |
| Dinoprostone | Vaginal suppository |
| Estradiol | Vaginal ring |
| Estradiol | Vaginal tablet |
| Clotrimazole | Vaginal tablet |
| Ethinyl estradiol/etonogestrel | Vaginal ring |
| Levonorgestrel | Intrauterine device |
| Miconazole nitrate | Vaginal suppository |
| Progesterone | Vaginal insert |
| Terconazole | Vaginal suppository |
| Metronidazole | Vaginal gel |
| Miconazole | Vaginal gel |
The advantages of using IUDs:
- It helps to minimize Systemic side effects.
- GIT irritations associated with some drugs can be avoided.
- Bioavailability can be enhanced.
- The first-pass metabolism can be avoided.
- Contact with digestive fluid is avoided, thereby preventing enzymatic degradation of some medicines.
- Can be self-administered by the patient.
- Absorption enhancer excipients can be used to overcome the problems of bioavailability of larger drug molecules.